Difference between revisions of "OB intent concepts"
(→Perception) |
(→Attribution in perception) |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
*[[Stereotyping]]. Judging someone on the basis of our perception of the group to which that person belongs. | *[[Stereotyping]]. Judging someone on the basis of our perception of the group to which that person belongs. | ||
*[[Stereotype threat]]. The degree to which we internally agree with the generally negative stereotyped perceptions of our groups. | *[[Stereotype threat]]. The degree to which we internally agree with the generally negative stereotyped perceptions of our groups. | ||
| − | *[[Self-fulfilling prophecy]]. A situation in which a person inaccurately perceives a second person, and the resulting expectations cause the second person to behave in ways consistent with the original perception.<gallery mode="packed-hover" widths=300px> | + | *[[Self-fulfilling prophecy]]. A situation in which a person inaccurately perceives a second person, and the resulting expectations cause the second person to behave in ways consistent with the original perception. |
| + | <gallery mode="packed-hover" widths=300px> | ||
File:Attribution-theory.png|[[Attribution theory]] | File:Attribution-theory.png|[[Attribution theory]] | ||
File:Attribution-factors.png|[[Attribution factor]] | File:Attribution-factors.png|[[Attribution factor]] | ||
Revision as of 05:00, 2 December 2018
OB intent concepts are those concepts that are related to perception and decision-making researched in organizational behavior studies. The concepts below are taken from Organizational Behavior by Robbins and Judge (17th edition); Septem Artes Administrativi served as the primary source of illustrations.
Perception
- Perception. A process by which individuals organize and interpret their sensory impressions in order to give meaning to their environment.
Attribution in perception
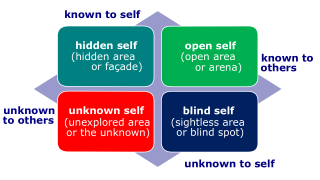
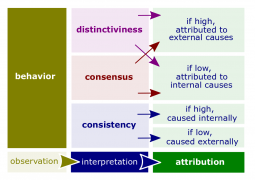
- Attribution theory. An attempt to determine whether an individual's behavior is internally or externally caused.
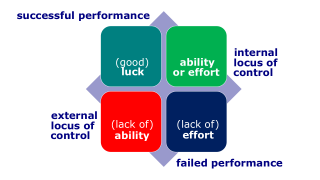
- Fundamental attribution error. The tendency to underestimate the influence of external factors and overestimate the influence of internal factors when making judgments about the behavior of others.
- Self-serving bias. The tendency for individuals to attribute their own successes to internal factors and put the blame for failures on external factors.
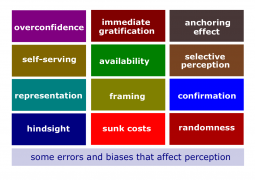
- Selective perception. The tendency to selectively interpret what one sees on the basis of one's interests, background, experience, and attitudes.
- Halo effect. The tendency to draw a general impression about an individual on the basis of a single characteristic.
- Contrast effect. Evaluation of a person's characteristics that is affected by comparisons with other people recently encountered who rank higher or lower on the same characteristics.
- Stereotyping. Judging someone on the basis of our perception of the group to which that person belongs.
- Stereotype threat. The degree to which we internally agree with the generally negative stereotyped perceptions of our groups.
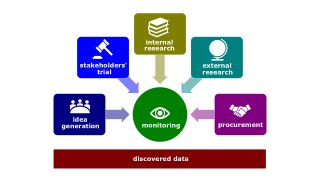
- Self-fulfilling prophecy. A situation in which a person inaccurately perceives a second person, and the resulting expectations cause the second person to behave in ways consistent with the original perception.
Decision making
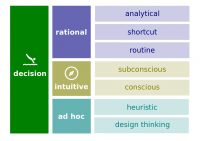
- Decision. A choice made from among two or more alternatives.
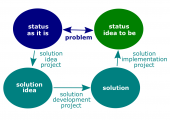
- Problem. A discrepancy between the current state of affairs and some desired state.
- Rationale. A reasoning characterized by making consistent, value-maximizing choices within specified constraints.
- Rational decision-making model. A decision-making model that describes how individuals should behave in order to maximize some outcome.
- Bounded rationality. A process of making decisions by constructing simplified models that extract the essential features from problems without capturing all their complexity.
- Intuitive decision making. An unconscious process created out of distilled experience.
- Anchoring bias. A tendency to fixate on initial information, from which one then falls to adequately adjust for subsequent information.
- Confirmation bias. The tendency to seek out information that reaffirms past choices and to discount information that contradicts past judgments.
- Availability bias. The tendency for people to base their judgments on information that is readily available to them.
- Escalation of commitment. An increased commitment to a previous decision in spite of negative information.
- Randomness error. The tendency of individuals to believe that they can predict the outcomes of random events.
- Risk aversion. The tendency to prefer a sure gain of a moderate amount over a riskier outcome, even if the riskier outcome might have a higher expected payoff.
- Hindsight bias. The tendency to believe falsely, after an outcome of an event is actually known, that one would have accurately predicted that outcome.
- Utilitarianism. A system in which decisions are made to provide the greatest good for the greatest number.
- Whistle-blower. An individual who reports unethical practices by their employer to outsiders.
- Behavioral ethics. Analyzing how people actually behave when confronted with ethical dilemmas.
- Creativity. The ability to produce novel and useful ideas.
- Three-stage model of creativity. The proposition that creativity involves three stages: causes (creative potential and creative environment), creative behavior, and creative outcomes (innovation).
- Problem formulation. The stage of creative behavior that involves identifying a problem or opportunity requiring a solution that is as yet unknown.
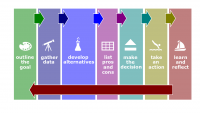
- Information gathering. The stage of creative behavior when possible solutions to a problem incubate in an individual's mind.
- Idea generation. The process of creative behavior that involves developing possible solutions to a problem from relevant information and knowledge.
- Idea evaluation. The process of creative behavior involving the evaluation of potential solutions to problems to identify the best one.