Difference between revisions of "Personalities and Work"
(→Key terms) |
(→Script) |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
===Script=== | ===Script=== | ||
| − | :Many [[psychologist]]s have studied the idea to match [[personality|personaliti]]es and [[occupation]]s. Logically, [[artist]]s tend to be more disruptive ''personalities'' that [[accountant]s. Vice versa, ''accountants'' tend to be more conforming ''personalities'' than [[artist]]s. | + | :Many [[psychologist]]s have studied the idea to match [[personality|personaliti]]es and [[occupation]]s. Logically, [[artist]]s tend to be more disruptive ''personalities'' that [[accountant]]s. Vice versa, ''accountants'' tend to be more conforming ''personalities'' than [[artist]]s. |
| − | : | + | :The [[Myers-Briggs Type Indicator]] ([[Myers-Briggs Type Indicator|MBTI]]) was originally developed to identify students' aptitudes toward various professions. This personality test taps four characteristics and classifies people into one of 16 personality types. Every characteristic contributes one letter from the following pairs: [[Extraversion]] ('''E''') or [[Intraversion]] ('''I''') depending on onward or inward focus, [[Sensing]] ('''S''') or [[Intuition]] ('''N''') depending on preference in taking in information, [[Thinking]] ('''T''') or [[Feeling]] ('''F''') depending on preference in making decisions, [[Judging]] ('''J''') or [[Perceiving]] ('''P''') depending on preference in living outer life. For instance, ''INFP'' would stand for ''intuitive, feeling, perceiving introvert''. |
| + | |||
| + | :Although many companies collect [[Myers-Briggs Type Indicator|MBTI]] data, this test has little to no effect in the workspace. A successful sport team, for instance, should be a mosaic of ''personalities'' regardless of the fact that all of them would share the same ''occupation''. | ||
are more disruptive, some are more conforming, some are more individual, some are more collective. American psychologist John Holland assumed that some [[occupation]]s require particular ''personalities'' and identified six categories that require specific ''personalities''. | are more disruptive, some are more conforming, some are more individual, some are more collective. American psychologist John Holland assumed that some [[occupation]]s require particular ''personalities'' and identified six categories that require specific ''personalities''. | ||
Revision as of 23:11, 4 May 2020
Personalities and Work (hereinafter, the Lectio) is the second lesson part of the Nature of Occupations lesson that introduces its participants to occupations and related topics.
This lesson belongs to the Introduction to Employment session of the CNM Cyber Orientation. The Orientation is the second stage of the WorldOpp Pipeline.
Contents
Content
The predecessor lectio is What Occupation Is.
Key terms
- Personality. The unique combination of emotional, thought, and behavioral patterns that affect how a person reacts to situations and interacts with others.
- Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI). A personality test that taps four characteristics and classifies people into one of 16 personality types. Every characteristic contributes one letter from the following pairs: Extraversion (E) or Intraversion (I) depending on onward or inward focus, Sensing (S) or Intuition (N) depending on preference in taking in information, Thinking (T) or Feeling (F) depending on preference in making decisions, Judging (J) or Perceiving (P) depending on preference in living outer life.
Script
- Many psychologists have studied the idea to match personalities and occupations. Logically, artists tend to be more disruptive personalities that accountants. Vice versa, accountants tend to be more conforming personalities than artists.
- The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) was originally developed to identify students' aptitudes toward various professions. This personality test taps four characteristics and classifies people into one of 16 personality types. Every characteristic contributes one letter from the following pairs: Extraversion (E) or Intraversion (I) depending on onward or inward focus, Sensing (S) or Intuition (N) depending on preference in taking in information, Thinking (T) or Feeling (F) depending on preference in making decisions, Judging (J) or Perceiving (P) depending on preference in living outer life. For instance, INFP would stand for intuitive, feeling, perceiving introvert.
- Although many companies collect MBTI data, this test has little to no effect in the workspace. A successful sport team, for instance, should be a mosaic of personalities regardless of the fact that all of them would share the same occupation.
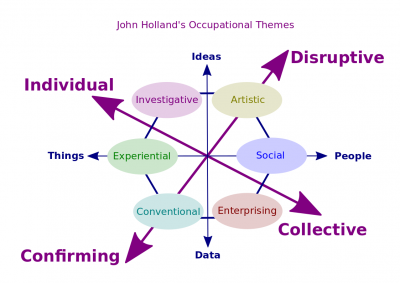
are more disruptive, some are more conforming, some are more individual, some are more collective. American psychologist John Holland assumed that some occupations require particular personalities and identified six categories that require specific personalities.
- Here are two different sets of dimensions, one is working ideas verses data and people verses things and clearly social works more with people and experiential or realistic work more with things. Ideas, we have artistic and investigative. So artistic basically create ideas and investigative find ideas or find what`s there behind the ideas and data. Enterprise and conventional, interestingly enterprising is not in ideas, enterprising is between people and data. It's more of persuasive, working with people and data. That's it for occupational themes. Next we will look at conditions of work.
Occupational Themes is the successor lectio.