Difference between revisions of "Decision-making"
(→Linear vs nonlinear) |
(→Programmed vs non-programmed) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
#'''[[Decision]]'''. A choice made from among two or more alternatives. | #'''[[Decision]]'''. A choice made from among two or more alternatives. | ||
#*[[Programmed decision]]. Any [[decision]] that is made while handling a [[structured task]]. These decisions are repetitive and can be handled by a routine approach. In [[enterprise]]s, [[programmed decision]]s are often made according to [[policy|polici]]es, [[operative rule]]s, etc. | #*[[Programmed decision]]. Any [[decision]] that is made while handling a [[structured task]]. These decisions are repetitive and can be handled by a routine approach. In [[enterprise]]s, [[programmed decision]]s are often made according to [[policy|polici]]es, [[operative rule]]s, etc. | ||
| − | #*[[Non-programmed decision]] ([[Non-programmed decision|creative decision]]). A unique and nonrecurring [[decision]] that requires a custom-made solution. | + | #*[[File:Discretion.png|400px|thumb|right|[[Decisional discretion]]]][[Non-programmed decision]] ([[Non-programmed decision|creative decision]]). A unique and nonrecurring [[decision]] that requires a custom-made solution. |
| + | |||
| + | #'''[[Decision criteria]]'''. Criteria that define what's important or relevant to resolving a problem. | ||
| + | #*[[Quantitative approach in management]]. The use of quantitative techniques to improve [[decision-making]]. | ||
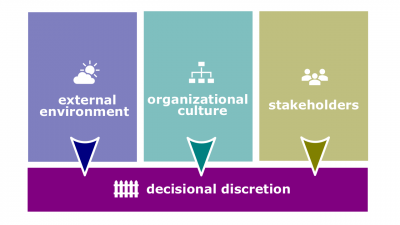
| + | #*[[Decisional discretion]]. The freedom to decide what should be done in a particular situation. | ||
===Individual vs collective=== | ===Individual vs collective=== | ||
Revision as of 18:32, 14 June 2020
Decision-making (alternatively spelled, decision making) is the action or process of making decisions, especially, creative behavior resulted in a non-programmed decision.
Classifications
Programmed vs non-programmed
- Decision. A choice made from among two or more alternatives.
- Programmed decision. Any decision that is made while handling a structured task. These decisions are repetitive and can be handled by a routine approach. In enterprises, programmed decisions are often made according to policies, operative rules, etc.
- Non-programmed decision (creative decision). A unique and nonrecurring decision that requires a custom-made solution.
- Decision criteria. Criteria that define what's important or relevant to resolving a problem.
- Quantitative approach in management. The use of quantitative techniques to improve decision-making.
- Decisional discretion. The freedom to decide what should be done in a particular situation.
Individual vs collective
- Individual decision-making. Decision-making made by an individual as opposed to group decision-making.
Approaches
- Decision-making approach. A particular manner of taking preliminary steps toward making a decision.
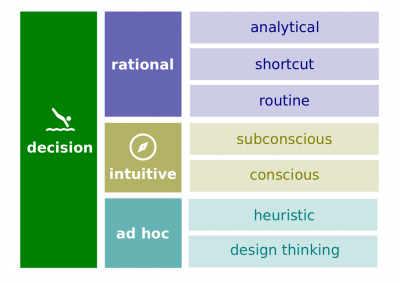
Intuitive
Rational
Ad hoc
Tendencies
Optimizing vs. satisficing
Conservative vs aggressive
Process types
Agile vs rigid
Linear vs nonlinear
- Intuitive decision-making. Unconscious decision-making on the basis of distilled experience, feelings, and accumulated judgment.
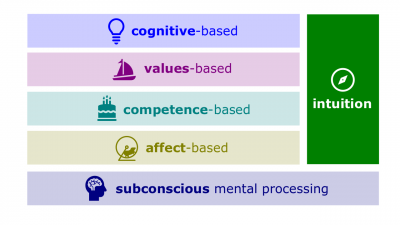
- Intuition. An instinctive feeling not necessarily supported by research.
- Rational decision-making. Decision-making that produces choices that are logical and consistent and maximize value.
- Rationale. A reasoning characterized by making consistent, value-maximizing choices within specified constraints.
- Controlled expectancy. A situation in which a decision maker is able to estimate the likelihood of certain outcomes.
- Certainty. A situation in which a decision maker can make accurate decisions because all outcomes are known.
- Uncertainty. A situation in which a decision maker has neither certainty nor reasonable probability estimates available.
- Ad hoc decision-making.
- Design thinking. Approaching management problems as designers approach design problems.
- Heuristic. A rule of thumb that decision makers use to simplify decision-making.
- Core self-evaluation. Bottom-line conclusions individuals have about their capacities, competence, and worth as a person. In other words, self-believing in one's inner worth and basic competence.
- General mental ability. An overall factor of intelligence, as suggested by the positive correlations among specific intellectual ability dimensions.
- Decisional tendency.
- Bounded rationality. Decision-making that is rational, but limited (bounded) by an individual's ability to process information. In other words, bounded rationality is a process of making decisions by constructing simplified models that extract the essential features from problems without capturing all their complexity.
- Escalation of commitment. An increased commitment to a previous decision despite evidence it may have been wrong.
- Risk aversion. The tendency to prefer a sure gain of a moderate amount over a riskier outcome, even if the riskier outcome might have a higher expected payoff.
- Decision-making dilemma. Optimizing vs. satisficing, intuitive vs rational vs ad hoc, Agile vs rigid, conservative vs aggressive, linear vs nonlinear
- Satisfice. Acceptance of solutions that are "good enough."
- Allostasis. Working to change behavior and attitude to find stability.
Considerations
Self-regulation
- Self-regulation strategy.
- Prevention focus. A self-regulation strategy that involves striving for goals by fulfilling duties and obligations.
- Promotion focus. A self-regulation strategy that involves striving for goals through advancement and accomplishment.
Ethics
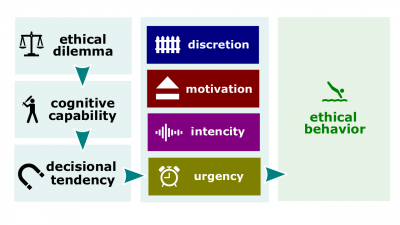
- Ethical dilemma. A situation in which individuals are required to define right and wrong conduct.
- Ethics. Principles, values, and beliefs that define what is right and wrong behavior.
- Behavioral ethics. Analyzing how people actually behave when confronted with ethical dilemmas.