Difference between revisions of "OB communication concepts"
(→Communication process) |
(→Communication process) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
==Communication process== | ==Communication process== | ||
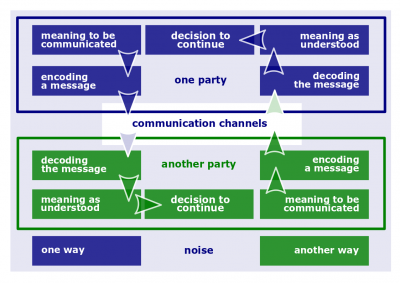
| − | *[[Communication process]]. The steps between a source and a receiver that results in the transfer and understanding of meaning. | + | *[[File:Communication-process.png|400px|thumb|right|[[Communication process]]]][[Communication process]]. The steps between a source and a receiver that results in the transfer and understanding of meaning. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Communication factors== | ==Communication factors== | ||
| Line 27: | Line 24: | ||
*[[Grapevine]]. An organization's informal communication network. | *[[Grapevine]]. An organization's informal communication network. | ||
*[[Channel richness]]. The amount of information that can be transmitted during a communication episode. | *[[Channel richness]]. The amount of information that can be transmitted during a communication episode. | ||
| − | <gallery widths=300px> | + | <gallery mode="packed-hover" widths=300px> |
File:Hierarchical-communication.png|[[Hierarchical communication]] | File:Hierarchical-communication.png|[[Hierarchical communication]] | ||
File:Chain-network.png|[[Chain network]] | File:Chain-network.png|[[Chain network]] | ||
Latest revision as of 20:44, 2 December 2018
OB communication concepts are those concepts that are related to communication researched in organizational behavior studies. The concepts below are taken from Organizational Behavior by Robbins and Judge (17th edition); Septem Artes Administrativi served as the primary source of illustrations.
Contents
Communication
- Communication. The transfer and the understanding of meaning.
Communication process
- Communication process. The steps between a source and a receiver that results in the transfer and understanding of meaning.
Communication factors
- Need for cognition. A personality trait of individuals depicting the ongoing desire to think and learn.
- Filtering. A sender's manipulation of information so that it will be seen more favorably by the receiver.
- Information overload. A condition in which information inflow exceeds an individual's processing capacity.
- Communication apprehension. Undue tension and anxiety about oral communication, written communication, or both.
Communication channels
- Formal channel. A communication channel established by an organization to transmit messages related to the professional activities of members.
- Informal channel. A communication channel that is created spontaneously and that emerges as a response to individual choices.
- Grapevine. An organization's informal communication network.
- Channel richness. The amount of information that can be transmitted during a communication episode.
Mode of processing
- Automatic processing. A relatively superficial consideration of evidence and information making use of heuristics.
- Controlled processing. A detailed consideration of evidence and information relying on facts, figures, and logic.
Context culture
- High-context culture. A culture that relies heavily on nonverbal and subtle situational cues in communication.
- Low-context culture. A culture that relies heavily on words to convey meaning in communication.