Difference between revisions of "Process"
(→Related coursework) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
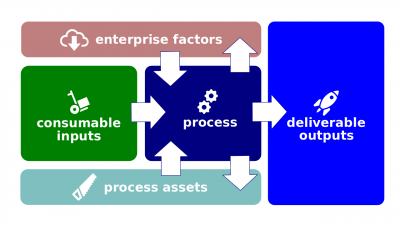
| − | [[File:Process.png|400px|thumb|right|[[Process]]]][[Process]] (hereinafter, the ''Process'') is a sequenced series, predefined, empiric, and/or merely chaotic, of [[activity|activiti]]es undertaken in order to achieve particular results | + | [[File:Process.png|400px|thumb|right|[[Process]]]][[Process]] (hereinafter, the ''Process'') is a sequenced series, predefined, empiric, and/or merely chaotic, of [[activity|activiti]]es undertaken in order to achieve particular results. [[Effort engineering]] defines that those ''activities'' convert [[input]]s into desired [[output]]s utilizing some [[process asset]]s such as tools and [[technique]]s and while being influenced by some [[enterprise factor]]s. |
| + | |||
| + | [[Process]]es may be repetitive or ad-hoc ways of work. Non-repetitive [[process]]es are called [[management process]]es. Repetitive [[process]]es that are performed by people for [[enterprise]]s are called [[business process]]es; those of their sets that produce a [[deliverable]] are called [[operations]]. Repetitive [[process]]es that are performed by [[system]]s including computers, robots, and/or machines are called [[system process]]es. | ||
| − | |||
==Definitions== | ==Definitions== | ||
Revision as of 17:24, 14 May 2020
Process (hereinafter, the Process) is a sequenced series, predefined, empiric, and/or merely chaotic, of activities undertaken in order to achieve particular results. Effort engineering defines that those activities convert inputs into desired outputs utilizing some process assets such as tools and techniques and while being influenced by some enterprise factors.
Processes may be repetitive or ad-hoc ways of work. Non-repetitive processes are called management processes. Repetitive processes that are performed by people for enterprises are called business processes; those of their sets that produce a deliverable are called operations. Repetitive processes that are performed by systems including computers, robots, and/or machines are called system processes.
Definitions
According to Organizational Behavior by Robbins and Judge (17th edition),
- Process. An action that individuals, groups, and organizations engage in as a result of inputs and that leads to certain outcomes.