Difference between revisions of "Occupational Interests"
(→Script) |
(→Script) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
===Script=== | ===Script=== | ||
| − | : | + | :Some [[personality|personaliti]]es are more disruptive, some are more conforming, some are more individual, some are more collective. American psychologist John Holland assumed that some [[occupation]]s require particular ''personalities'' and identified six categories that require specific ''personalities''. |
| − | + | :[[Realistic occupation]]s frequently involve work activities that include practical, hands-on problems and solutions. These workers often deal with plants, animals, and real-world materials like wood, tools, and machinery. Many of the [[occupation]]s require working outside and do not involve a lot of paperwork or working closely with others. Examples of that type of [[occupation]]s may include a carpenter, [[engineer]], farmer, [[operator]], [[technician]], [[tester]], and [[trades worker]]. Collectively, they may be called "doers;" in ancient times, they would have been hunters. | |
| − | : | ||
| − | + | :[[Investigative occupation]]s involve working with [[idea]]s and requires an extensive amount of thinking. These [[occupation]]s can involve searching for facts and figuring out problems mentally. Examples of that type of [[occupation]]s may include an auditor, [[business analyst]], [[compliance officer]], [[cost estimator]], [[editor]], inspector, [[interviewer]], and lawyer. Collectively, they may be called "thinkers;" in ancient times, they would have been shamans. | |
| − | :Investigative | ||
| − | Artistic | + | :[[Artistic occupation]]s involve working with forms, designs and patterns. They often require self-expression and the work can be done without following a clear set of rules. Examples of that type of [[occupation]]s may include an artist, composer, creative writer, designer, [[enterprise architect]], and [[originator]]. Collectively, they may be called "innovators;" in ancient times, they would have been artisans. |
| − | |||
| − | + | :[[Social occupation]]s involve working with, communicating with, and teaching people. These [[occupation]]s often involve helping or providing service to others. Examples of that type of [[occupation]]s may include a [[career counselor]], [[job coach]], [[mediator]], sales representative, [[service worker]], and teacher. Collectively, they may be called "helpers;" in ancient times, they would have been healers. | |
| − | :Social occupation | + | :*'''[[Enterprising occupation]]''' ([[Enterprising occupation|persuasive occupation]]). An [[occupation]] that frequently involves starting up and carrying out [[project]]s. These [[occupation]]s can involve leading people and making many decisions. Sometimes they require risk taking and often deal with business. Examples of that type of [[occupation]]s may include an [[architect]], [[product owner]], and [[self-employed]]. Collectively, they may be called "creators;" in ancient times, they would have been leaders. |
| − | + | :*'''[[Conventional occupation]]''' ([[Conventional occupation|conforming occupation]]). An [[occupation]] that frequently involves following set procedures and routines. These [[occupation]]s can include working with data and details more than with ideas. Usually there is a clear line of authority to follow. Examples of that type of [[occupation]]s may include an [[accountant]], [[assistant]], [[bookkeeper]], [[clerk]], [[document management specialist]], [[laborer]], and technical writer. Collectively, they may be called "organizers;" in ancient times, they would have been guardians. | |
| − | Enterprising | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Conventional | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
'''[[Personalities in Trade]]''' is the successor [[lectio]]. | '''[[Personalities in Trade]]''' is the successor [[lectio]]. | ||
==Quiz== | ==Quiz== | ||
Revision as of 19:30, 4 May 2020
Occupational Themes (hereinafter, the Lectio) is the second lesson part of the Nature of Occupations lesson that introduces its participants to occupations and related topics.
This lesson belongs to the Introduction to Employment session of the CNM Cyber Orientation. The Orientation is the second stage of the WorldOpp Pipeline.
Contents
Content
The predecessor lectio is What Occupation Is.
Key terms
- Holland Occupational Themes. Consultant, manager, specialist.
- Realistic occupation. An occupation that frequently involves work activities that include practical, hands-on problems and solutions. They often deal with plants, animals, and real-world materials like wood, tools, and machinery. Many of the occupations require working outside and do not involve a lot of paperwork or working closely with others. Examples of that type of occupations may include a carpenter, engineer, farmer, operator, technician, tester, and trades worker. Collectively, they may be called "doers;" in ancient times, they would have been hunters.
- Investigative occupation (intellectual occupation). An occupation that frequently involves working with ideas and requires an extensive amount of thinking. These occupations can involve searching for facts and figuring out problems mentally. Examples of that type of occupations may include an auditor, business analyst, compliance officer, cost estimator, editor, inspector, interviewer, and lawyer. Collectively, they may be called "thinkers;" in ancient times, they would have been shamans.
- Artistic occupation (esthetic occupation). An occupation that frequently involves working with forms, designs and patterns. They often require self-expression and the work can be done without following a clear set of rules. Examples of that type of occupations may include an artist, composer, creative writer, designer, enterprise architect, and originator. Collectively, they may be called "innovators;" in ancient times, they would have been artisans.
- Social occupation (supportive occupation). An occupation that frequently involves working with, communicating with, and teaching people. These occupations often involve helping or providing service to others. Examples of that type of occupations may include a career counselor, job coach, mediator, sales representative, service worker, and teacher. Collectively, they may be called "helpers;" in ancient times, they would have been healers.
- Enterprising occupation (persuasive occupation). An occupation that frequently involves starting up and carrying out projects. These occupations can involve leading people and making many decisions. Sometimes they require risk taking and often deal with business. Examples of that type of occupations may include an architect, product owner, and self-employed. Collectively, they may be called "creators;" in ancient times, they would have been leaders.
- Conventional occupation (conforming occupation). An occupation that frequently involves following set procedures and routines. These occupations can include working with data and details more than with ideas. Usually there is a clear line of authority to follow. Examples of that type of occupations may include an accountant, assistant, bookkeeper, clerk, document management specialist, laborer, and technical writer. Collectively, they may be called "organizers;" in ancient times, they would have been guardians.
Script
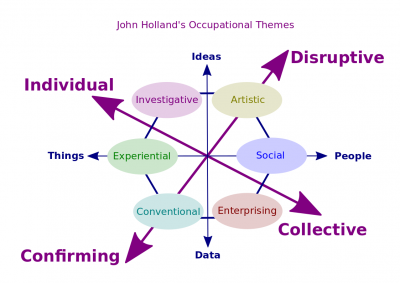
- Some personalities are more disruptive, some are more conforming, some are more individual, some are more collective. American psychologist John Holland assumed that some occupations require particular personalities and identified six categories that require specific personalities.
- Realistic occupations frequently involve work activities that include practical, hands-on problems and solutions. These workers often deal with plants, animals, and real-world materials like wood, tools, and machinery. Many of the occupations require working outside and do not involve a lot of paperwork or working closely with others. Examples of that type of occupations may include a carpenter, engineer, farmer, operator, technician, tester, and trades worker. Collectively, they may be called "doers;" in ancient times, they would have been hunters.
- Investigative occupations involve working with ideas and requires an extensive amount of thinking. These occupations can involve searching for facts and figuring out problems mentally. Examples of that type of occupations may include an auditor, business analyst, compliance officer, cost estimator, editor, inspector, interviewer, and lawyer. Collectively, they may be called "thinkers;" in ancient times, they would have been shamans.
- Artistic occupations involve working with forms, designs and patterns. They often require self-expression and the work can be done without following a clear set of rules. Examples of that type of occupations may include an artist, composer, creative writer, designer, enterprise architect, and originator. Collectively, they may be called "innovators;" in ancient times, they would have been artisans.
- Social occupations involve working with, communicating with, and teaching people. These occupations often involve helping or providing service to others. Examples of that type of occupations may include a career counselor, job coach, mediator, sales representative, service worker, and teacher. Collectively, they may be called "helpers;" in ancient times, they would have been healers.
- Enterprising occupation (persuasive occupation). An occupation that frequently involves starting up and carrying out projects. These occupations can involve leading people and making many decisions. Sometimes they require risk taking and often deal with business. Examples of that type of occupations may include an architect, product owner, and self-employed. Collectively, they may be called "creators;" in ancient times, they would have been leaders.
- Conventional occupation (conforming occupation). An occupation that frequently involves following set procedures and routines. These occupations can include working with data and details more than with ideas. Usually there is a clear line of authority to follow. Examples of that type of occupations may include an accountant, assistant, bookkeeper, clerk, document management specialist, laborer, and technical writer. Collectively, they may be called "organizers;" in ancient times, they would have been guardians.
Personalities in Trade is the successor lectio.