Human Perceptions Quarter
Human Perceptions Quarter (hereinafter, the Quarter) is a lecture introducing the learners to individuals discovery primarily through key topics related to perception. The Quarter is the first of four lectures of Individuals Quadrivium, which is the fourth of seven modules of Septem Artes Administrativi (hereinafter, the Course). The Course is designed to introduce the learners to general concepts in business administration, management, and organizational behavior.
Contents
Outline
Operations Management Quarter is the predecessor lecture. In the enterprise discovery series, the previous lecture is Monitoring Quarter.
- Individuals discovery is data discovery conducted by human beings. This data is either stored in brains or sensed from external environments. This particular lecture concentrates on human perceptions because this method is instrumental for collecting data that routinely emerges.
Concepts
- Perception. A process by which individuals organize and interpret their sensory impressions in order to give meaning to their environment.
- Psychology. The science that seeks to measure, explain, and sometimes change the behavior of humans and other animals.
- Sense. (1) A faculty by which the body perceives an external stimulus; one of the faculties of sight, smell, hearing, taste, and touch; (2) A feeling that something is the case.
- Cognitive capability. Power or ability to perceive and understand external environment and its processes.
- Physical ability. An individual's capacity to do tasks that demand stamina, dexterity, strength, and similar characteristics.
- Heredity. Factors determined at conception; one's biological, physiological, and inherent psychological makeup.
- Intellectual ability. An individual's capacity to do mental activities -- thinking, reasoning, and problem solving constrained by human limitations particularly expressed by the Allegory of the Cave.
- Information overload. A condition in which information inflow exceeds an individual's processing capacity.
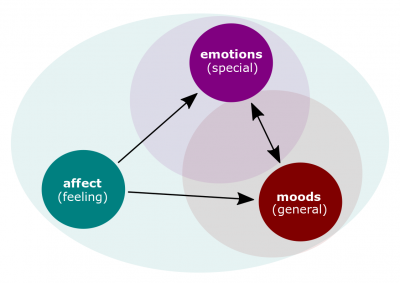
- Affect. A broad range of feelings that people experience.
- Positive affect. A mood dimension that consists of specific positive emotions such as excitement, enthusiasm, and elation at the high end.
- Negative affect. A mood dimension that consists of specific negative emotions such as nervousness, stress, and anxiety at the high end.
- Affect intensity. Individual differences in the strength with which individuals experience their emotions.
- Psychological mood. Feelings that tend to be less intense than emotions and that lack a contextual stimulus.
- Positivity offset. The tendency of most individuals to experience a mildly positive mood at zero input (when nothing in particular is going on).
- Emotion. Intense feeling that is directed at someone or something.
- Felt emotion. An individual's actual emotions.
- Displayed emotion. An emotion that is organizationally required and considered appropriate in a given job.
- Moral emotion. An emotion that have moral implications.
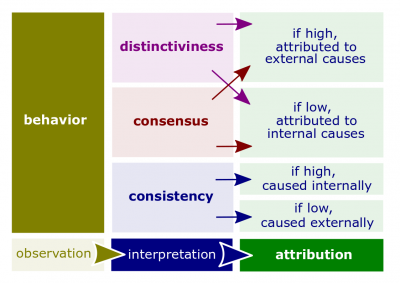
- Attribution theory. A theory used to explain how we judge people differently depending on what meaning we attribute to a given behavior. This theory also attempts to determine whether an individual's behavior is internally or externally caused.
Factors Observation Interpretation Attribution Distinctiveness The individual behaves this way in other situations Low distinctiveness Internal The individual behaves differently in other situations High distinctiveness External Consensus Other people behave the same way in similar situations High consensus External Other people behave differently in similar situations Low consensus Internal Consistency The individual behaves this way consistently High consistency Internal The individual behaves this way rarely Low consistency External - Fundamental attribution error. The tendency to underestimate the influence of external factors and overestimate the influence of internal factors when making judgments about the behavior of others.
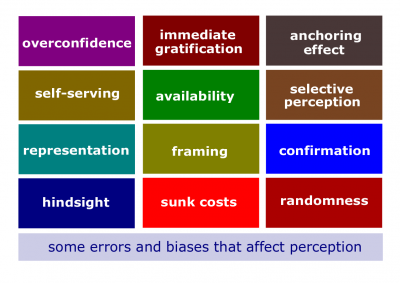
- Self-serving bias. The tendency for individuals to attribute their own successes to internal factors while putting the blame for failures on external factors.
- Attribution factor. One of three factors that determine attribution of observed behavior to external or internal causes under the attribution theory.
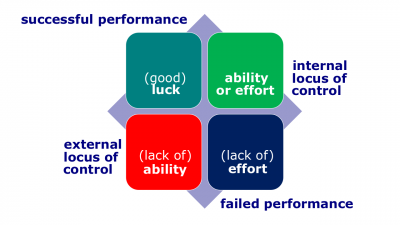
- Locus of control. A personality attribute that measures the degree to which people believe they control their own fate.
- Reaffirmation tendency. An inclination toward favorable perception of something that reaffirms one's attitudes.
- Confirmation bias. The tendency to seek out information that reaffirms past choices and to discount information that contradicts past judgments.
- Selective perception. The tendency to selectively interpret what one sees on the basis of one's interests, background, experience, and attitudes.
- Self-fulfilling prophecy. A situation in which a person inaccurately perceives a second person, and the resulting expectations cause the second person to behave in ways consistent with the original perception.
- Perception shortcut. A shorter alternative route in cognitive processing.
- Bias. A tendency or preference toward a particular perspective or ideology.
- Hindsight bias. The tendency to believe falsely, after an outcome of an event is actually known, that one would have accurately predicted that outcome.
- Anchoring bias. A tendency to fixate on initial information, from which one then falls to adequately adjust for subsequent information.
- Availability bias. The tendency for people to base their judgments on information that is readily available to them.
- Assumed similarity. The assumption that others are like oneself.
- Randomness error. The tendency of individuals to believe that they can predict the outcomes of random events.
- Halo effect. The tendency to draw a general impression about an individual on the basis of a single characteristic.
- Contrast effect. Evaluation of a person's characteristics that is affected by comparisons with other people recently encountered who rank higher or lower on the same characteristics.
- Illusory correlation. The tendency of people to associate two events when in reality there is no connection.
- Personality. The unique combination of emotional, thought, and behavioral patterns that affect how a person reacts to situations and interacts with others.
- Emotional stability. A personality dimension that characterizes someone as calm, self-confident, and secure (positive) versus nervous, depressed, and insecure (negative).
- Openness to experience. A personality dimension that characterizes someone in terms of imagination, sensitivity, and curiosity.
- Agreeableness. A personality dimension that describes someone who is good natured, cooperative, and trusting.
- Ego strength. A personality measure of the strength of a person's convictions.
- Conscientiousness. A personality dimension that describes someone who is responsible, dependable, persistent, and organized.
- Extraversion. A personality dimension describing someone who is sociable, gregarious, and assertive.
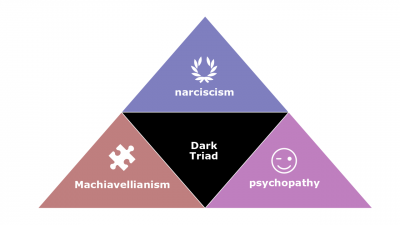
- Dark Triad. A constellation of negative personality traits consisting of Machiavellianism, narcissism, and psychopathy.
- Narcissism. The tendency to be arrogant, have a grandiose sense of self-importance, require excessive admiration, and have a sense of entitlement.
- Psychopathy. The tendency for a lack of concern for others and lack of guilt or remorse when actions cause harm.
- Machiavellianism. The degree to which an individual is pragmatic, maintains emotional distance, and believes that ends can justify means.
- Personality trait. An enduring characteristic that describes an individual's behavior.
- Proactive personality. A personality trait that describes individuals who are more prone to take actions to influence their environments. These individuals identify opportunities, show initiative, and persevere until meaningful change occurs.
- Self-monitoring. A personality trait that measures an individual's ability to adjust his or her behavior to external, situational factors.
- Type A personality. People who have a chronic sense of urgency and an excessive competitive drive.
- Type B personality. People who are relaxed and easygoing and accept change easily.
- Trait activation theory. A theory that predicts that some situations, events, or interventions "activate" a trait more than others.
- Situation strength theory. A theory indicating that the way personality translates into behavior depends on the strength of the situation.
- Self-esteem. (1) Confidence in one's own worth or abilities; (2) Self-respect; (3) An individual's degree of like or dislike for herself or himself.
- Self-concept. An idea of the self constructed from the beliefs one holds about oneself and the responses of others.
- Core value (collectively, also known as values). A basic conviction that a specific mode of conduct or end-state of existence is personally or socially preferable to an opposite or converse mode of conduct or end-state of existence.
- Values. Basic convictions about what is right and wrong.
- Instrumental value. A preferable mode of behavior or mean of achieving one's terminal values.
- Terminal value. A desirable end-state of existence; the goal a person would like to achieve during his or her lifetime.
- Values system. A hierarchy based on a ranking of an individual's values in terms of their intensity.
- Self-concordance. The degree to which people's reasons for pursuing goals are consistent with their interests and core values.
Roles
- Counseling psychologist. A professional who assesses and evaluates individuals' problems through the use of case history, interview, and observation and provides individual or group counseling services to assist individuals or employers in achieving more effective personal, social, educational, and vocational development and adjustment.
Methods
- Self-efficacy change. The researcher who developed self-efficacy theory, Albert Bandura, proposes four ways self-efficacy can be increased:
- Divided line. A method of cognitive classification based on the analogy of the divided line.
Instruments
- Johari Window. A tool used to illustrate and improve self-awareness, and mutual understanding between individuals within a group. Johari Window can also be used to assess and improve a group's relationship with other groups.
- Big Five Model. A personality trait model that includes extraversion, agreeableness, conscientiousness, emotional stability, and openness to experience.
- Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI). A personality test that taps four characteristics and classifies people into one of 16 personality types.
Practices
- No known concept, technique, or instrument can fully predict someone's perceptions, motivations, decisions, or behavior. Based on the practice, Big Five Model grants better results than MBTI; nonetheless, MBTI remains the most popular instrument, probably, because of its simplicity.
Human Motivations Quarter is the successor lecture. In the enterprise discovery series, the next lecture is Communication Quarter.