Enterprise resource planning ecosystem
An enterprise resource planning ecosystem (alternatively known as enterprise resource planning system, ERP system, ERP systems, and ERP suite; hereinafter, the Ecosystem) is the system of systems that are designed to facilitate enterprise resource planning (ERP). Often, the lower-level systems are called ERP modules.
The Ecosystems are designed to seamlessly integrate business processes throughout the entire enterprise and across various functions such as accounting, bookkeeping, customer relationship management (CRM), human resource, inventory, marketing, procurement, sales, and order management usually in realtime. ERP software commonly powers this integration.
Contents
System of systems
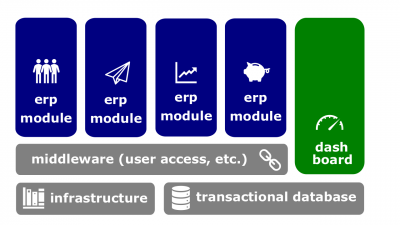
One or more shared databases is the central feature of all Ecosystems. All the business processes and any operations that involve enterprise resources are translated into financial transactions in order to streamline those transactions within one unified ecosystem.
Reporting and automation
- The Ecosystems tend to offer some degree of synchronized reporting and automation. Instead of forcing employees to maintain separate databases and spreadsheets that have to be manually merged to generate reports, some ERP solutions allow staff to pull reports from one system. For instance, with sales orders automatically flowing into the financial system without any manual re-keying, the order management department can process orders more quickly and accurately, and the finance department can close the books faster. Other common ERP features include a portal or dashboard to enable employees to quickly understand the business' performance on key metrics.
Business value
- At its core, ERP helps employees do their jobs more efficiently by breaking down barriers between business units. More specifically, an ERP solution can:
- Give a global, real-time view of data that can enable companies to address concerns proactively and drive improvements.
- Improve financial compliance with regulatory standards and reduces risk.
- Automate core business operations such as lead-to-cash, order-to-fulfillment, and procure-to-pay processes.
- Enhance customer service by providing one source for billing and relationship tracking.
Components
- Transactional database. Any database that is able to accommodate transactions related to the conducting of business, especially buying or selling.
- Management dashboard. The panel containing instruments and controls that a software user is able to utilize.
- ERP module. A module of an enterprise resource planning ecosystem.
Related concepts
- Enterprise middleware. Middleware that provides all software applications with data and/or services.