Difference between revisions of "Sprint"
(→Related coursework) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
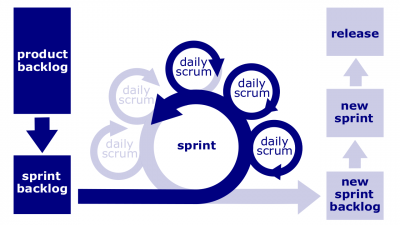
[[File:Scrum.png|400px|thumb|right|[[Sprint]]]]In [[Agile methodology]], [[Sprint]] is a fixed-length time period during which a [[milestone]] is expected to be reached. Usually, one [[user story]] or [[product backlog item]] (PBI) must be transformed into a potentially shippable [[deliverable]] and ready for review. Each [[sprint]] is assigned a set amount of time to be accomplished (sometimes referred to as [[timebox]]), which could be anywhere from one week to one month, but typically lasts two weeks. In the [[Agile methodology]], [[Sprint]]s are referred as [[iteration]]s. | [[File:Scrum.png|400px|thumb|right|[[Sprint]]]]In [[Agile methodology]], [[Sprint]] is a fixed-length time period during which a [[milestone]] is expected to be reached. Usually, one [[user story]] or [[product backlog item]] (PBI) must be transformed into a potentially shippable [[deliverable]] and ready for review. Each [[sprint]] is assigned a set amount of time to be accomplished (sometimes referred to as [[timebox]]), which could be anywhere from one week to one month, but typically lasts two weeks. In the [[Agile methodology]], [[Sprint]]s are referred as [[iteration]]s. | ||
| + | ==Related concepts== | ||
*[[Sprint goal]] (aka [[Sprint theme]]). The key focus of the work for a single sprint. | *[[Sprint goal]] (aka [[Sprint theme]]). The key focus of the work for a single sprint. | ||
Revision as of 12:36, 4 January 2019
In Agile methodology, Sprint is a fixed-length time period during which a milestone is expected to be reached. Usually, one user story or product backlog item (PBI) must be transformed into a potentially shippable deliverable and ready for review. Each sprint is assigned a set amount of time to be accomplished (sometimes referred to as timebox), which could be anywhere from one week to one month, but typically lasts two weeks. In the Agile methodology, Sprints are referred as iterations.
Related concepts
- Sprint goal (aka Sprint theme). The key focus of the work for a single sprint.