Strategic business unit
(Redirected from New 4Ps)
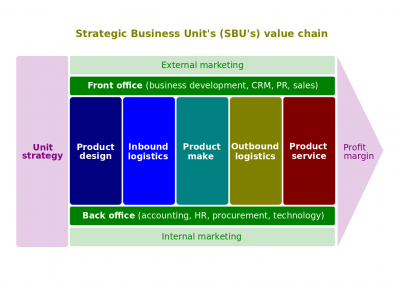
Strategic business unit (commonly known by its acronym, SBU; hereinafter, SBU) is a single independent business of an enterprise that formulates its own competitive strategy.
Contents
Definition
According to Management by Robbins and Coulter (14th edition),
- Strategic business unit. A single independent business of an organization that formulates its own competitive strategy.
According to the Corporate Strategy by Lynch (4th edition),
- Strategic business unit (SBU). The level of a multibusiness unit at which the strategy needs to be developed. The unit has the responsibility for determining the strategy of that unit. An SBU is not necessarily the same as a division of the company: there may be more than one SBU within a division and SBUs may combine elements from more than one division.
New 4Ps
The concept of holistic marketing prompted some marketers to spread marketing endeavors throughout the whole business. Although the New 4Ps is not a marketable tool per se, its idea is to align every endeavor within the business with the marketing objectives.
People
- People implies two sides. On the one side, the employees are critical to marketing success since any marketing is as great as company's employees are. That also captions the internal marketing notion. On the other side, consumers are people and the business objective is to understand their lives more broadly, and not just view them as shoppers who consume market exchangeables.
Processes
- Processes reflects all the processes within the business, including imaginatively generating insights and breakthrough products, services, and marketing activities.
Programs
- Programs encompasses the old four Ps as well as a range of other marketing activities that might not fit as neatly into the old view of marketing.
Performance
- Performance implies two sides. On the one side, it measures financial such as profitability and non-monetary such as brand and customer equity implications within the business. On the other side, it measures the impact beyond the business itself. That may include social responsibility, as well as legal, ethical, and environmental outcomes.