Difference between revisions of "Operations Management Quarter"
(→Concepts) |
|||
| (191 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[Operations Management Quarter]] (hereinafter, the ''Quarter'') is the | + | [[Operations Management Quarter]] (hereinafter, the ''Quarter'') is a lecture introducing the learners to [[operations management]]. The ''Quarter'' is the last of four lectures of [[Operations Quadrivium]], which is the third of seven modules of '''[[Septem Artes Administrativi]]''' (hereinafter, the ''Course''). The ''Course'' is designed to introduce the learners to general concepts in [[business administration]], [[management]], and [[organizational behavior]]. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Outline== | ==Outline== | ||
| − | '' | + | ''[[Effort Engineering Quarter]] is the predecessor lecture. In the [[enterprise planning]] series, the previous lecture is [[Project Management Quarter]].'' |
===Concepts=== | ===Concepts=== | ||
| − | #'''[[ | + | #'''[[Operations management]]'''. (1) Practice and a set of concepts, based on that practice, that define culture of managing of [[operations]]; (2) A group who is responsible for overseeing all aspects of a customer's production resources. |
| + | #*[[Operations]]. [[Enterprise effort]]s undertaken in order to create some [[deliverable]]s using some [[process]]es. | ||
| + | #*[[Ongoing operation]]s. Repetitive [[enterprise effort]]s undertaken in order to create specified [[deliverable]]s using already designed [[process]]es. | ||
| + | #'''[[Enterprise operation]]'''. | ||
| + | #*[[Management]]. Coordinating and overseeing the work activities of others so their activities are completed efficiently and effectively. | ||
| + | #*[[Organizing]]. [[Management function]] that involves arranging and structuring work to accomplish the [[enterprise goal]]s. [[Organizing]] include determining what [[job task]]s are to be done, who is to do them, how the tasks are to be grouped, who reports to whom, and where decisions are to be made. | ||
| + | #*[[Compliance management]]. Management of [[regulatory compliance]] for a particular [[business]] and/or at a particular [[enterprise]]. | ||
| + | #*[[Corrective action]]. Changes made to bring expected future performance of the project in line with the plan. | ||
| + | #'''[[Job task]]'''. The lowest level of [[enterprise effort]]. In [[Agile methodology]], a [[job task|task]] is a single unit of work broken down from a [[user story]]. In [[project management]], a [[job task|task]] is a generic term for work that is not included in the work breakdown structure, but potentially could be a further decomposition of work by the individuals responsible for that work. A [[job task]] is usually completed by just one person and is a part of an [[activity]]. | ||
| + | #*[[Task identity]]. The degree to which a job requires completion of a whole and identifiable piece of work. | ||
| + | #*[[Task significance]]. The degree to which a job has a substantial impact on the lives or work of other people. | ||
| + | #*[[Task performance]]. The combination of [[effectiveness]] and [[efficiency]] at doing core job tasks. | ||
| + | #'''[[Task structure]]'''. One of Fiedler's situational contingencies that describes the degree to which job assignments are formalized and structured. | ||
| + | #*[[Structured task]]. | ||
| + | #*[[Unstructured task]]. | ||
| + | #'''[[Sprint task]]'''. A single small item of work that helps one particular story reach completion. | ||
| + | #*[[Task list]]. A list of tasks needed to complete the set of stories committed to a sprint. | ||
| + | #*[[Task board]]. A physical or online visual representation of user stories broken down into tasks or work units. A physical task board can be as simple as a whiteboard with three columns labeled To Do, Doing, and Done; colored post-it notes or index cards representing tasks are placed in the column that reflects the task's current state. A task board can be expanded to hold more columns and can also include horizontal swim lanes. | ||
| + | #'''[[Traditional goal-setting]]'''. An approach to setting goals in which top managers set goals that then flow down through the organization and become subgoals for each organizational area. | ||
| + | #*[[Span of control]]. The number of employees a manager is directly responsible for. | ||
| + | #'''[[Chain of command]]'''. The unbroken line of [[authority]] that extends from the top of the organization to the lowest echelon and clarifies who reports to whom. | ||
| + | #*[[Responsibility]]. The obligation of expectation to perform any assigned duties. | ||
| + | #*[[Human resource planning]]. Ensuring that the organization has the right number and kinds of capable people in the right places and at the right times. | ||
| + | #'''[[Value chain management]]'''. The process of managing the sequence of activities and information along the entire value chain. | ||
| + | #*[[Business process management]] ([[Business process management|BPM]]). A holistic management approach focused on aligning all aspects of an organization with the wants and needs of clients. BPM attempts to improve processes continuously. It can, therefore, be described as a "process optimization process". It is argued that BPM enables organizations to be more efficient, effective and capable of change than a functionally focused, traditional hierarchical management approach. | ||
| + | #*[[Business development]]. The activity of pursuing strategic opportunities for a particular [[business]] or [[enterprise]], for example by cultivating partnerships or other commercial relationships, or identifying new markets for its products or services. | ||
| + | #'''[[Management responsibility]]'''. The state or fact of managers having a duty to deal with enterprise challenges and/or of having control over subordinates. | ||
#*[[Symbolic view of management responsibility]]. The view that much of an organization's success or failure is due to external forces outside managers' control. | #*[[Symbolic view of management responsibility]]. The view that much of an organization's success or failure is due to external forces outside managers' control. | ||
#*[[Omnipotent view of management responsibility]]. The view that managers are directly responsible for an organization's success or failure. | #*[[Omnipotent view of management responsibility]]. The view that managers are directly responsible for an organization's success or failure. | ||
| − | #'''[[ | + | #'''[[Management function]]'''. An activity or purpose natural to a [[manager]]. |
| − | #*[[ | + | #*[[Socioeconomic view of management function]]. The view that management's social responsibility goes beyond making profits to include protecting and improving society's welfare. |
| − | + | #*[[Classical view of management function]]. The view that management's only social responsibility is to maximize profits. | |
| − | #*[[ | + | #'''[[Universality of management]]'''. The reality that management is needed in all types and sizes of organizations, at all organizational levels, in all organizational areas, and in organizations no matter where located. |
| − | + | #*[[Diversity management]]. The [[process]] and programs by which [[manager]]s make everyone more aware of and sensitive to the needs and differences of others. | |
| − | + | #'''[[Management approach]]'''. | |
| − | + | #*[[Classical approach in management concepts]]. First studies of management, which emphasized nationality and making organizations and workers as efficient as possible. | |
| − | + | #*[[Scientific management]]. An approach that involves using the scientific method to find the "one best way" for a job to be done. | |
| − | + | #*[[General administrative theory]]. An approach to management that focuses on describing what managers do and what constitutes good management practice. | |
| − | + | #*[[Contingency approach]]. A management approach that recognizes organizations as different, which means they face different situations (contingencies) and require different ways of managing. | |
| − | + | #*[[Contingency variable]]. A situational factor that moderates the relationship between two or more variables. | |
| − | *[[ | + | #*[[Management by objectives]]. A program that encompasses specific mutually agreed-upon goals with feedback on goal progress. |
| − | + | #*[[Management by walking around]]. A term used to describe when a manager is out in the work area interacting directly with employees. | |
| − | + | #*[[Evidence-based management]]. The systematic use of the best available evidence to improve management practice. | |
| − | + | #*[[Green management]]. [[Management]] in which managers consider the impact of their organization on the natural environment. | |
| − | |||
| − | *[[Classical approach in management concepts]]. First studies of management, which emphasized nationality and making organizations and workers as efficient as possible. | ||
| − | *[[ | ||
| − | *[[ | ||
| − | *[[Contingency approach]]. A management approach that recognizes organizations as different, which means they face different situations (contingencies) and require different ways of managing. | ||
| − | *[[Contingency variable]]. A situational factor that moderates the relationship between two or more variables. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | *[[Management by objectives]]. A | ||
| − | |||
| − | *[[Management by walking around]]. A term used to describe when a manager is out in the work area interacting directly with employees. | ||
| − | *[[ | ||
| − | *[[ | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Roles=== | ===Roles=== | ||
| − | #'''[[ | + | #'''[[Managerial role]]'''. A specific action or behavior expected of and exhibited by a [[manager]]. |
| − | # | + | #*[[Decisional role]]. A [[managerial role]] that revolves around making choices. [[Henry Mintzberg]] identified the following four [[decisional role]]s: [[negotiator]], [[resource allocator]], [[disturbance handler]], and [[entrepreneur]].<blockquote><table class="wikitable" width=100% style="text-align:center;"><tr><td>Level</td><th colspan="4">[[Decisional role]]</th></tr><tr><th>[[Non-manager|Non‑manager]]</th><td rowspan="4">'''[[Negotiator]]'''</td><td>Rarely, [[Resource allocator|allocator]]</td><td rowspan="4">[[Disturbance handler|Disturbance '''handler''']]</td><td rowspan="3">Rarely, [[visionary]]</td></tr><tr><th>[[Frontline manager|Frontline]]</th><td rowspan="3">[[Resource allocator|Resource '''allocator''']]</td></tr><tr><th>[[Middle manager|Middle]]</th></tr><tr><th>[[Top officer|Top]]</th><td>'''[[Visionary]]'''</td></tr></table></blockquote> |
| + | #*[[Informational role]]. A [[managerial role]] that involves collecting, receiving, and disseminating information. [[Henry Mintzberg]] identified the following three [[informational role]]s: [[monitor]], [[disseminator]], and [[spokeperson]].<blockquote><table class="wikitable" width=100% style="text-align:center;"><tr><td>Level</td><th colspan="3">[[Informational role]]</th></tr><tr><th>[[Non-manager|Non‑manager]]</th><td rowspan="4">'''[[Monitor]]'''</td><td rowspan="4">'''[[Disseminator]]'''</td><td rowspan="2">Rarely, [[spokeperson]]</td></tr><tr><th>[[Frontline manager|Frontline]]</th></tr><tr><th>[[Middle manager|Middle]]</th><td rowspan="2">'''[[Spokeperson]]'''</td></tr><tr><th>[[Top officer|Top]]</th></tr></table></blockquote> | ||
| + | #*[[Interpersonal role]]. A [[managerial role]] that involves people and other duties that are ceremonial and symbolic in nature. [[Henry Mintzberg]] identified the following three [[interpersonal role]]s: [[figurehead]], [[leader]], and [[liaison]].<blockquote><table class="wikitable" width=100% style="text-align:center;"><tr><td>Level</td><th colspan="3">[[Interpersonal role]]</th></tr><tr><th>[[Non-manager|Non‑manager]]</th><td>Rarely, [[figurehead]]</td><td>Rarely, [[influencer]]</td><td rowspan="4">'''[[Liaison]]'''</td></tr><tr><th>[[Frontline manager|Frontline]]</th><td rowspan="3">'''[[Figurehead]]'''</td><td rowspan="3">'''[[Influencer]]'''</td></tr><tr><th>[[Middle manager|Middle]]</th></tr><tr><th>[[Top officer|Top]]</th></tr></table></blockquote> | ||
| + | #[[File:Management-levels.png|400px|thumb|right|[[Manager]]s]]'''[[Manager]]'''. (1) An individual who achieves goals through other people; (2) Someone who coordinates and oversees the work of other people so organizational goals can be accomplished. | ||
#*[[Frontline manager]] (or first-line manager). A [[manager]] at the lowest levels of the [[organizational structure]] who manage the work of nonmanagerial employees. | #*[[Frontline manager]] (or first-line manager). A [[manager]] at the lowest levels of the [[organizational structure]] who manage the work of nonmanagerial employees. | ||
#*[[Middle manager]]. A [[manager]] between the lowest and upper levels of the [[organizational structure]] who manage the work of [[frontline manager]]s. | #*[[Middle manager]]. A [[manager]] between the lowest and upper levels of the [[organizational structure]] who manage the work of [[frontline manager]]s. | ||
| + | #'''[[Functional manager]]'''. A manager responsible for activities in a specialized department or function (e.g., engineering, manufacturing, marketing). | ||
| + | #*[[Line manager]]. (1) The manager of any group that actually makes a product or performs a service. (2) A functional manager. | ||
===Methods=== | ===Methods=== | ||
| + | #'''[[Disciplinary action]]'''. An action taken by a manager to enforce the organization's work standards and regulations. | ||
| + | #*[[Basic corrective action]]. Corrective action that looks at how and why performance deviated before correcting the source of deviation. | ||
| + | #*[[Immediate corrective action]]. Corrective action that corrects problems at once to get performance back on track. | ||
| + | #*[[Progressive disciplinary action]]. An approach to ensure that the minimum penalty appropriate to the offense is imposed. | ||
| + | #'''[[Schedule compression]]'''. A group of techniques used to shorten the [[schedule]] without reducing the [[scope]]. The ''compression'' is not always possible and often requires an increase in the cost. | ||
| + | #*[[Crashing]]. The [[schedule compression]] that increases the cost. | ||
| + | #*[[Parallel tracking]]. The [[schedule compression]] by overlapping tasks and activities that would normally be done in sequence. Performing [[enterprise effort]]s in parallel may increase [[risk]]s. | ||
| + | #'''[[Unity of command]]'''. The managerial technique that ensures unity of effort under one responsible person (or commander) for completing a [[job task]]. In other words, [[unity of command]] is a principle, which idea is to make sure that each employee reports to one and only one superior to whom he or she is directly responsible. | ||
| + | #'''[[Unstructured-task technique]]'''. An established [[procedure]] for resolving completely new [[job task]]s or [[job task]]s requiring working in [[unstructured environment]]s. | ||
| + | #*[[Pair working]]. A scenario where two [[team member]]s share a single workstation and work together to develop a single feature. | ||
| + | #*[[Swarming]]. Mutual work of team members with appropriate skills work together to complete a task that a team member is having trouble completing on his or her own. | ||
| + | |||
===Instruments=== | ===Instruments=== | ||
| + | #'''[[Unified Process]]'''. A customizable framework developed for [[enterprise administration]]. This ''framework'' emphasizes (a) four [[project life-cycle phase]]s, in which (b) six "engineering" disciplines such as business modeling, requirements, design, implementation, test, and [[deployment]] are applied, as well as (c) the [[strategic development tripod]]. | ||
| + | #*[[Rational Unified Process]] (RUP). The version of the [[Unified Process]] that is trademarked by [[IBM]]. | ||
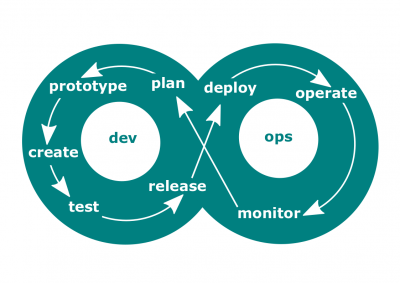
| + | #[[File:Devops.png|400px|thumb|right|[[DevOps process]]]]'''[[DevOps]]'''. Practice and a set of concepts, based on that practice, that define culture of utilizing the [[DevOps process]] to unify development (Dev) and operations (Ops). | ||
| + | #*[[DevOps process]]. A framework used in [[DevOps]] that represents a chain of operational phases such as (a) Code, (b) Build, (c) Test, (d) Package, (e) Release, (f) Configure, and (e) Monitor. | ||
| + | #*[[DevOps toolchain]]. A framework used in [[DevOps]] that represents a chain of tools, each of which fits one of the phases of a [[DevOps process]]. | ||
| + | #'''[[Software upgrade]]'''. The replacement of a software product with a newer, improved version. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Results=== | ||
| + | #'''[[Operational plan]]'''. A [[plan]] that encompasses a particular operational area of the organization. | ||
| + | #'''[[Intention for bid]]''' ([[IFB]]). Communications, written or oral by the prospective sources showing their willingness to perform the specified work. This could be a letter, statement of qualifications or response to a request for proposal. | ||
| + | |||
===Practices=== | ===Practices=== | ||
| − | '' | + | ''[[Human Perceptions Quarter]] is the successor lecture. In the [[enterprise planning]] series, the next lecture is [[Talent Management Quarter]].'' |
==Materials== | ==Materials== | ||
| Line 85: | Line 99: | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Septem Artes Administrativi]][[Category:Lecture notes]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:20, 28 April 2023
Operations Management Quarter (hereinafter, the Quarter) is a lecture introducing the learners to operations management. The Quarter is the last of four lectures of Operations Quadrivium, which is the third of seven modules of Septem Artes Administrativi (hereinafter, the Course). The Course is designed to introduce the learners to general concepts in business administration, management, and organizational behavior.
Contents
Outline
Effort Engineering Quarter is the predecessor lecture. In the enterprise planning series, the previous lecture is Project Management Quarter.
Concepts
- Operations management. (1) Practice and a set of concepts, based on that practice, that define culture of managing of operations; (2) A group who is responsible for overseeing all aspects of a customer's production resources.
- Operations. Enterprise efforts undertaken in order to create some deliverables using some processes.
- Ongoing operations. Repetitive enterprise efforts undertaken in order to create specified deliverables using already designed processes.
- Enterprise operation.
- Management. Coordinating and overseeing the work activities of others so their activities are completed efficiently and effectively.
- Organizing. Management function that involves arranging and structuring work to accomplish the enterprise goals. Organizing include determining what job tasks are to be done, who is to do them, how the tasks are to be grouped, who reports to whom, and where decisions are to be made.
- Compliance management. Management of regulatory compliance for a particular business and/or at a particular enterprise.
- Corrective action. Changes made to bring expected future performance of the project in line with the plan.
- Job task. The lowest level of enterprise effort. In Agile methodology, a task is a single unit of work broken down from a user story. In project management, a task is a generic term for work that is not included in the work breakdown structure, but potentially could be a further decomposition of work by the individuals responsible for that work. A job task is usually completed by just one person and is a part of an activity.
- Task identity. The degree to which a job requires completion of a whole and identifiable piece of work.
- Task significance. The degree to which a job has a substantial impact on the lives or work of other people.
- Task performance. The combination of effectiveness and efficiency at doing core job tasks.
- Task structure. One of Fiedler's situational contingencies that describes the degree to which job assignments are formalized and structured.
- Sprint task. A single small item of work that helps one particular story reach completion.
- Task list. A list of tasks needed to complete the set of stories committed to a sprint.
- Task board. A physical or online visual representation of user stories broken down into tasks or work units. A physical task board can be as simple as a whiteboard with three columns labeled To Do, Doing, and Done; colored post-it notes or index cards representing tasks are placed in the column that reflects the task's current state. A task board can be expanded to hold more columns and can also include horizontal swim lanes.
- Traditional goal-setting. An approach to setting goals in which top managers set goals that then flow down through the organization and become subgoals for each organizational area.
- Span of control. The number of employees a manager is directly responsible for.
- Chain of command. The unbroken line of authority that extends from the top of the organization to the lowest echelon and clarifies who reports to whom.
- Responsibility. The obligation of expectation to perform any assigned duties.
- Human resource planning. Ensuring that the organization has the right number and kinds of capable people in the right places and at the right times.
- Value chain management. The process of managing the sequence of activities and information along the entire value chain.
- Business process management (BPM). A holistic management approach focused on aligning all aspects of an organization with the wants and needs of clients. BPM attempts to improve processes continuously. It can, therefore, be described as a "process optimization process". It is argued that BPM enables organizations to be more efficient, effective and capable of change than a functionally focused, traditional hierarchical management approach.
- Business development. The activity of pursuing strategic opportunities for a particular business or enterprise, for example by cultivating partnerships or other commercial relationships, or identifying new markets for its products or services.
- Management responsibility. The state or fact of managers having a duty to deal with enterprise challenges and/or of having control over subordinates.
- Symbolic view of management responsibility. The view that much of an organization's success or failure is due to external forces outside managers' control.
- Omnipotent view of management responsibility. The view that managers are directly responsible for an organization's success or failure.
- Management function. An activity or purpose natural to a manager.
- Socioeconomic view of management function. The view that management's social responsibility goes beyond making profits to include protecting and improving society's welfare.
- Classical view of management function. The view that management's only social responsibility is to maximize profits.
- Universality of management. The reality that management is needed in all types and sizes of organizations, at all organizational levels, in all organizational areas, and in organizations no matter where located.
- Diversity management. The process and programs by which managers make everyone more aware of and sensitive to the needs and differences of others.
- Management approach.
- Classical approach in management concepts. First studies of management, which emphasized nationality and making organizations and workers as efficient as possible.
- Scientific management. An approach that involves using the scientific method to find the "one best way" for a job to be done.
- General administrative theory. An approach to management that focuses on describing what managers do and what constitutes good management practice.
- Contingency approach. A management approach that recognizes organizations as different, which means they face different situations (contingencies) and require different ways of managing.
- Contingency variable. A situational factor that moderates the relationship between two or more variables.
- Management by objectives. A program that encompasses specific mutually agreed-upon goals with feedback on goal progress.
- Management by walking around. A term used to describe when a manager is out in the work area interacting directly with employees.
- Evidence-based management. The systematic use of the best available evidence to improve management practice.
- Green management. Management in which managers consider the impact of their organization on the natural environment.
Roles
- Managerial role. A specific action or behavior expected of and exhibited by a manager.
- Decisional role. A managerial role that revolves around making choices. Henry Mintzberg identified the following four decisional roles: negotiator, resource allocator, disturbance handler, and entrepreneur.
Level Decisional role Non‑manager Negotiator Rarely, allocator Disturbance handler Rarely, visionary Frontline Resource allocator Middle Top Visionary - Informational role. A managerial role that involves collecting, receiving, and disseminating information. Henry Mintzberg identified the following three informational roles: monitor, disseminator, and spokeperson.
Level Informational role Non‑manager Monitor Disseminator Rarely, spokeperson Frontline Middle Spokeperson Top - Interpersonal role. A managerial role that involves people and other duties that are ceremonial and symbolic in nature. Henry Mintzberg identified the following three interpersonal roles: figurehead, leader, and liaison.
Level Interpersonal role Non‑manager Rarely, figurehead Rarely, influencer Liaison Frontline Figurehead Influencer Middle Top
- Decisional role. A managerial role that revolves around making choices. Henry Mintzberg identified the following four decisional roles: negotiator, resource allocator, disturbance handler, and entrepreneur.
- Manager. (1) An individual who achieves goals through other people; (2) Someone who coordinates and oversees the work of other people so organizational goals can be accomplished.
- Frontline manager (or first-line manager). A manager at the lowest levels of the organizational structure who manage the work of nonmanagerial employees.
- Middle manager. A manager between the lowest and upper levels of the organizational structure who manage the work of frontline managers.
- Functional manager. A manager responsible for activities in a specialized department or function (e.g., engineering, manufacturing, marketing).
- Line manager. (1) The manager of any group that actually makes a product or performs a service. (2) A functional manager.
Methods
- Disciplinary action. An action taken by a manager to enforce the organization's work standards and regulations.
- Basic corrective action. Corrective action that looks at how and why performance deviated before correcting the source of deviation.
- Immediate corrective action. Corrective action that corrects problems at once to get performance back on track.
- Progressive disciplinary action. An approach to ensure that the minimum penalty appropriate to the offense is imposed.
- Schedule compression. A group of techniques used to shorten the schedule without reducing the scope. The compression is not always possible and often requires an increase in the cost.
- Crashing. The schedule compression that increases the cost.
- Parallel tracking. The schedule compression by overlapping tasks and activities that would normally be done in sequence. Performing enterprise efforts in parallel may increase risks.
- Unity of command. The managerial technique that ensures unity of effort under one responsible person (or commander) for completing a job task. In other words, unity of command is a principle, which idea is to make sure that each employee reports to one and only one superior to whom he or she is directly responsible.
- Unstructured-task technique. An established procedure for resolving completely new job tasks or job tasks requiring working in unstructured environments.
- Pair working. A scenario where two team members share a single workstation and work together to develop a single feature.
- Swarming. Mutual work of team members with appropriate skills work together to complete a task that a team member is having trouble completing on his or her own.
Instruments
- Unified Process. A customizable framework developed for enterprise administration. This framework emphasizes (a) four project life-cycle phases, in which (b) six "engineering" disciplines such as business modeling, requirements, design, implementation, test, and deployment are applied, as well as (c) the strategic development tripod.
- Rational Unified Process (RUP). The version of the Unified Process that is trademarked by IBM.
- DevOps. Practice and a set of concepts, based on that practice, that define culture of utilizing the DevOps process to unify development (Dev) and operations (Ops).
- DevOps process. A framework used in DevOps that represents a chain of operational phases such as (a) Code, (b) Build, (c) Test, (d) Package, (e) Release, (f) Configure, and (e) Monitor.
- DevOps toolchain. A framework used in DevOps that represents a chain of tools, each of which fits one of the phases of a DevOps process.
- Software upgrade. The replacement of a software product with a newer, improved version.
Results
- Operational plan. A plan that encompasses a particular operational area of the organization.
- Intention for bid (IFB). Communications, written or oral by the prospective sources showing their willingness to perform the specified work. This could be a letter, statement of qualifications or response to a request for proposal.
Practices
Human Perceptions Quarter is the successor lecture. In the enterprise planning series, the next lecture is Talent Management Quarter.