Difference between revisions of "Education Essentials"
(→Summary) |
|||
| (30 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Cnm-digital.png|400px|thumb|right|[[CNMCyber suite]]s]]The [[Education Essentials]] (hereinafter, the ''Lesson'') is the [[lesson]] of [[CNMCyber]] that introduces its participants to the general and related concepts of [[education]]. The ''Lesson'' belongs to the '''[[Introduction to Education]]''' session of [[EmployableU Concepts]]. |
| − | + | The ''Lesson'' is made up of five [[lectio]]s. At [[CNMCyber]], the word, [[lectio]], is used for a lesson part. | |
| − | == | + | ==Summaries== |
| − | The | + | ===Predecessor=== |
| + | :The predecessor lesson is [[Workforce Services]]. | ||
| − | === | + | ===Outline=== |
| − | : | + | :{|class="wikitable" width=100% style="text-align:center;" |
| + | |+[[Education Essentials]] | ||
| + | |width=25%|[[Lectio]]s | ||
| + | !#!!Referred topics | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ![[What Learning Is]] | ||
| + | |1||[[Learning]], [[purposeful learning]], [[occasional learning]], [[observation]], [[observational learning]], [[social learning]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ![[What Education Is]] | ||
| + | |2||[[Education]], [[formal training]] ([[formal training|formal education]]), [[compulsory education]], [[individualized learning]], [[informal learning]], [[learning content]], [[lecture]], [[textbook]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ![[Educational Objectives]] | ||
| + | |3||[[Educational objective]], [[Bloom's taxonomy]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ![[What Training Is]] | ||
| + | |4||[[Training]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ![[Training Targets]] | ||
| + | |5||[[Development domain]], [[cognitive domain]], [[affective domain]], [[psychomotor domain]], [[training target]], [[zone of proximal development]] ([[Zone of proximal development|ZPD]]) | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Successor=== | ||
| + | :The successor lesson is [[Educational Methods]]. | ||
| − | + | ==2019 Education presentation== | |
| − | + | The video of the presentation is published on https://youtu.be/0uzVhrUtqxU (6:03). Here is its full text. | |
| − | : | ||
| − | : | ||
| − | : | + | ===Overview=== |
| − | + | :Welcome to ''Education Essentials''. In this brief presentation, we are going to take a look at [[education]] in general and the purposes of [[education]] including [[educational objective]]s and [[development domain]]s that [[education]] aims to target. Let's roll the sleeves. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
===What education is=== | ===What education is=== | ||
| + | :[[Education]] is the process and or product of facilitating ones’ acquisition of [[KSA]]s, [[knowledge, skills, and abilities]]. Most are familiar with formal education; this is a type of education which is formally approved by a government or some accreditation body. If you studied at school, the school`s program was approved by the government or some agency. Some part of formal education which is called compulsory education is a mandatory, so usually it`s imposed by the government and with some exceptions required to some people. | ||
| − | + | :The formal education will include school and university, but compulsory education usually includes just school or a part of the school. Fortunately, or unfortunately formal education is not the only, it is probably the lowest, the minor part of what we learn or how we learn or how we educate ourselves with someone’s help or without and let`s say this lecture is not a part of formal education. If we will get to a more formal training then it will be approved by some accreditation body but for now this lecture is not a part of a school program, it`s not a part of a college, it`s just for you to get a glimpse of what we are about to offer. | |
| − | |||
| − | The formal education will include school and university, but compulsory education usually includes just school or a part of the school. Fortunately, or unfortunately formal education is not the only, it is probably the lowest, the minor part of what we learn or how we learn or how we educate ourselves with someone’s help or without and let`s say this lecture is not a part of formal education. If we will get to a more formal training then it will be approved by some accreditation body but for now this lecture is not a part of a school program, it`s not a part of a college, it`s just for you to get a glimpse of what we are about to offer. | ||
| − | Education has its objectives, an education objective is a goal of gaining specified knowledge, skills and abilities by a learner as a result of specified learning activity or set of activities. There is no one single classification of different objectives but one. The most very popular came from works of American educator whose name was Benjamin Bloom. | + | ===Educational objectives=== |
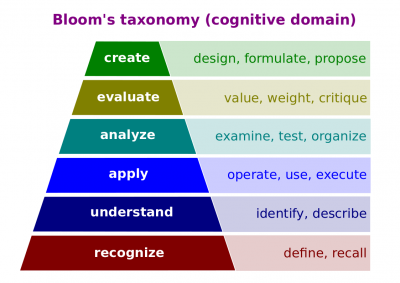
| + | :[[File:Blooms-taxonomy.png|400px|thumb|[[Bloom's taxonomy]]]]Education has its objectives, an education objective is a goal of gaining specified knowledge, skills and abilities by a learner as a result of specified learning activity or set of activities. There is no one single classification of different objectives but one. The most very popular came from works of American educator whose name was Benjamin Bloom. | ||
| − | + | :Let's take a look at cognitive domain of Bloom`s taxonomy of educational objectives, in the base of his pyramid he put recognize or later understand, apply further analyze, evaluate and create. Recognize is the beginning, so let`s say we are about to learn a new language and initially you start recognizing some words, “hello.” And you say, “hello.” You recognize it`s a greeting but you don`t know part of the speech. Later when you go, you can go to a more understanding part so then you can describe and you can identify, you can say hello is an informal greeting. There are more formal like good evening or good afternoon. Then you can apply or start applying, operate, use, execute later you can analyze, examine, test, organize. You can put let`s say, “hello Jenifer” or, “John.” Well you can say, “John hello.” So you can test, examine, put in different parts then you can evaluate, or value, weight, critique, say hello is probably not too appropriate, and here you say, “good afternoon senator John Foster” or whatever and at the top of the pyramid, right now it`s great which is designed from Bloom`s taxonomy. Initially taxonomy proposed by Benjamin Bloom, the last two parts of the pyramid was revised. Initially it was synthesizing and then evaluate but for our purposes, it does not matter too much. | |
| − | + | ===Development domains=== | |
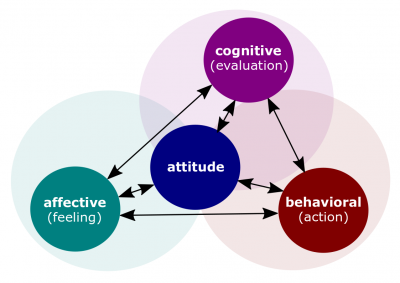
| + | :[[File:Attitude.png|400px|thumb|[[Attitude]]]]As fast as you note it discuss only cognitive domain but Benjamin Bloom identified three different domains and they coincide with attitude and so we talked about cognitive domain, which deals with knowledge, another domain which is effective which deals with emotions and here we are developing skills through hands on activities. Practice you will get some emotions or I like it or I don`t like it. | ||
| − | + | :There is the main, Benjamin Bloom called psychomotor domain. It deals with actions. Once again, knowledge, emotions and actions by Benjamin Bloom they were divided in three different domains. | |
===Summary=== | ===Summary=== | ||
| − | :This concludes the '' | + | :This concludes the ''Education Essentials'' presentation. We have defined [[education]] and used [[Bloom's taxonomy]] to take a look at [[educational objective]]s and [[development domain]]s. If you haven't done yet so, you are now welcome to move to [[Educational Methods]]. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category: Orientation Curriculum]][[Category:Presentations]] | [[Category: Orientation Curriculum]][[Category:Presentations]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:29, 29 October 2023
The Education Essentials (hereinafter, the Lesson) is the lesson of CNMCyber that introduces its participants to the general and related concepts of education. The Lesson belongs to the Introduction to Education session of EmployableU Concepts.
The Lesson is made up of five lectios. At CNMCyber, the word, lectio, is used for a lesson part.
Contents
Summaries
Predecessor
- The predecessor lesson is Workforce Services.
Outline
Successor
- The successor lesson is Educational Methods.
2019 Education presentation
The video of the presentation is published on https://youtu.be/0uzVhrUtqxU (6:03). Here is its full text.
Overview
- Welcome to Education Essentials. In this brief presentation, we are going to take a look at education in general and the purposes of education including educational objectives and development domains that education aims to target. Let's roll the sleeves.
What education is
- Education is the process and or product of facilitating ones’ acquisition of KSAs, knowledge, skills, and abilities. Most are familiar with formal education; this is a type of education which is formally approved by a government or some accreditation body. If you studied at school, the school`s program was approved by the government or some agency. Some part of formal education which is called compulsory education is a mandatory, so usually it`s imposed by the government and with some exceptions required to some people.
- The formal education will include school and university, but compulsory education usually includes just school or a part of the school. Fortunately, or unfortunately formal education is not the only, it is probably the lowest, the minor part of what we learn or how we learn or how we educate ourselves with someone’s help or without and let`s say this lecture is not a part of formal education. If we will get to a more formal training then it will be approved by some accreditation body but for now this lecture is not a part of a school program, it`s not a part of a college, it`s just for you to get a glimpse of what we are about to offer.
Educational objectives
- Education has its objectives, an education objective is a goal of gaining specified knowledge, skills and abilities by a learner as a result of specified learning activity or set of activities. There is no one single classification of different objectives but one. The most very popular came from works of American educator whose name was Benjamin Bloom.
- Let's take a look at cognitive domain of Bloom`s taxonomy of educational objectives, in the base of his pyramid he put recognize or later understand, apply further analyze, evaluate and create. Recognize is the beginning, so let`s say we are about to learn a new language and initially you start recognizing some words, “hello.” And you say, “hello.” You recognize it`s a greeting but you don`t know part of the speech. Later when you go, you can go to a more understanding part so then you can describe and you can identify, you can say hello is an informal greeting. There are more formal like good evening or good afternoon. Then you can apply or start applying, operate, use, execute later you can analyze, examine, test, organize. You can put let`s say, “hello Jenifer” or, “John.” Well you can say, “John hello.” So you can test, examine, put in different parts then you can evaluate, or value, weight, critique, say hello is probably not too appropriate, and here you say, “good afternoon senator John Foster” or whatever and at the top of the pyramid, right now it`s great which is designed from Bloom`s taxonomy. Initially taxonomy proposed by Benjamin Bloom, the last two parts of the pyramid was revised. Initially it was synthesizing and then evaluate but for our purposes, it does not matter too much.
Development domains
- As fast as you note it discuss only cognitive domain but Benjamin Bloom identified three different domains and they coincide with attitude and so we talked about cognitive domain, which deals with knowledge, another domain which is effective which deals with emotions and here we are developing skills through hands on activities. Practice you will get some emotions or I like it or I don`t like it.
- There is the main, Benjamin Bloom called psychomotor domain. It deals with actions. Once again, knowledge, emotions and actions by Benjamin Bloom they were divided in three different domains.
Summary
- This concludes the Education Essentials presentation. We have defined education and used Bloom's taxonomy to take a look at educational objectives and development domains. If you haven't done yet so, you are now welcome to move to Educational Methods.