Difference between revisions of "OB change concepts"
(→Organizational change) |
(→Organizational change) |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
*[[Restraining force]]. A force that hinders movement from the existing equilibrium ([[Kurt Lewin]]). | *[[Restraining force]]. A force that hinders movement from the existing equilibrium ([[Kurt Lewin]]). | ||
*[[Action research]]. A change process based on systematic collection of data and then selection of a change action based on what the analyzed data indicate. | *[[Action research]]. A change process based on systematic collection of data and then selection of a change action based on what the analyzed data indicate. | ||
| + | <gallery mode="packed-hover" widths=300px> | ||
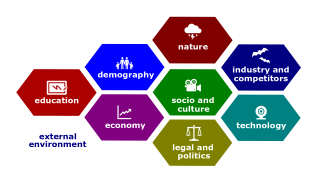
| + | File:External-environment.png|[[External environment]] | ||
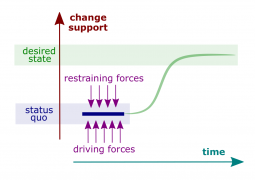
| + | File:Status-quo.png|[[Change-support analysis]] | ||
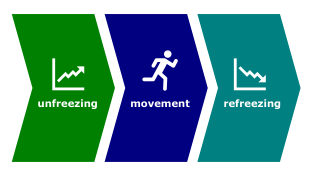
| + | File:Change-model.png|[[Change process model]] | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Organizational development== | ||
*[[Organizational development]]. A collection of [[planned change]] interventions, built on humanistic-democratic values, that seeks to improve organizational effectiveness and employee well-being. | *[[Organizational development]]. A collection of [[planned change]] interventions, built on humanistic-democratic values, that seeks to improve organizational effectiveness and employee well-being. | ||
*[[Sensitivity training]]. Training groups that seek to change behavior through unstructured group interaction. | *[[Sensitivity training]]. Training groups that seek to change behavior through unstructured group interaction. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 22: | ||
*[[Intergroup development]]. [[Organizational development]] efforts to change the attitudes, stereotypes, and perceptions that groups have of each other. | *[[Intergroup development]]. [[Organizational development]] efforts to change the attitudes, stereotypes, and perceptions that groups have of each other. | ||
*[[Appreciative inquiry]]. An approach that seeks to identify the unique qualities and special strengths of an organization, which can then be built on to improve performance. | *[[Appreciative inquiry]]. An approach that seeks to identify the unique qualities and special strengths of an organization, which can then be built on to improve performance. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Innovation== | ||
*[[Paradox theory]]. The theory that the key paradox in management is that there is no final status for an organization. | *[[Paradox theory]]. The theory that the key paradox in management is that there is no final status for an organization. | ||
*[[Innovation]]. A new idea applied to initiating or improving a product, process, or service. | *[[Innovation]]. A new idea applied to initiating or improving a product, process, or service. | ||
*[[Idea champion]]. An individual who takes an [[innovation]] and actively and enthusiastically promote the idea, build support, overcome resistance, and ensure that the idea is implemented. | *[[Idea champion]]. An individual who takes an [[innovation]] and actively and enthusiastically promote the idea, build support, overcome resistance, and ensure that the idea is implemented. | ||
*[[Learning organization]]. An [[organization]] that has developed the continuous capacity to adapt and change. | *[[Learning organization]]. An [[organization]] that has developed the continuous capacity to adapt and change. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Stress management== | ==Stress management== | ||
Latest revision as of 21:23, 2 December 2018
OB change concepts are those concepts that are related to organizational change and psychological stress researched in organizational behavior studies. The concepts below are taken from Organizational Behavior by Robbins and Judge (17th edition); Septem Artes Administrativi served as the primary source of illustrations.
Contents
Organizational change
- Organizational change. Making things different.
- Planned change. Change activities that are intentional and goal oriented.
- Change agent. A person who acts as a catalyst and assumes the responsibility for managing change activities.
- Driving force. A force that directs behavior away from status quo (Kurt Lewin).
- Restraining force. A force that hinders movement from the existing equilibrium (Kurt Lewin).
- Action research. A change process based on systematic collection of data and then selection of a change action based on what the analyzed data indicate.
Organizational development
- Organizational development. A collection of planned change interventions, built on humanistic-democratic values, that seeks to improve organizational effectiveness and employee well-being.
- Sensitivity training. Training groups that seek to change behavior through unstructured group interaction.
- Survey feedback. The use of questionnaires to identify discrepancies among member perceptions; discussion follows, and remedies are suggested.
- Process consultation. A meeting in which a consultant assists a client in understanding process events with which he or she must deal and identifying processes that need improvement.
- Intergroup development. Organizational development efforts to change the attitudes, stereotypes, and perceptions that groups have of each other.
- Appreciative inquiry. An approach that seeks to identify the unique qualities and special strengths of an organization, which can then be built on to improve performance.
Innovation
- Paradox theory. The theory that the key paradox in management is that there is no final status for an organization.
- Innovation. A new idea applied to initiating or improving a product, process, or service.
- Idea champion. An individual who takes an innovation and actively and enthusiastically promote the idea, build support, overcome resistance, and ensure that the idea is implemented.
- Learning organization. An organization that has developed the continuous capacity to adapt and change.
Stress management
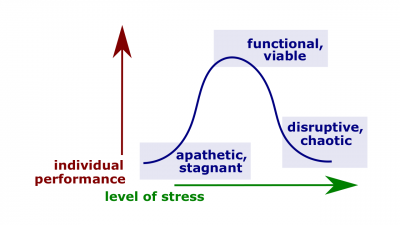
- Stress. An unpleasant psychological process that occurs in response to environmental pressures.
- Challenge stressor. A stressor associated with workload, pressure to complete tasks, and time urgency.
- Hindrance stressor. A stressor that keep you from reaching your goals (for example, red tape, office politics, confusion over job responsibilities).
- Work demand. A responsibility, pressure, obligation, and even uncertainty that individuals face in the workplace.
- Work resource. A thing within an individual's control that can be used to solve work demands.
- Allostasis. Working to change behavior and attitude to find stability.
- Wellness program. An organizationally supported program that focuses on the employee's total physical and mental condition.